CNC machining yields accurate results, yet conventional cutting tools are limited technically. Even the best carbide-coated tool has micro-defects formed on the surface. Cutting edges wear rapidly and affect machining accuracy, reducing tool life and tend to post-finishing demands. In contemporary manufacturing, these issues result in increased uptime, expenditures, and extended production times.
CNC diamond milling is an effective way to overcome these issues. Even single-crystal diamond tools will reach surface roughness values of less than 10 nm and figure errors of less than 10-5. The cutting sharpness of diamonds is much better and long-lasting than tooling in old times due to their extreme hardness. This allows manufacturing optical-grade surfaces on metals, polymers, and non-ferrous materials without secondary polishing. At ProleanTech, we use diamond milling to produce precise and clean parts such as gears, molds, and machine components.
This article has all the details of CNC diamond milling. You will see how the tools are designed, the processes that define the technique, and the industries that rely on it.
How Diamond Milling Improves Parts’ Surface Finish?

The tool's hardness directly affects how smooth the surface will be after machining. Diamond remains the top choice of this scale. The extreme hardness gives diamond cutting tools properties no other material can match. Synthetic diamonds also handle high heat and heavy cutting conditions. These features make them reliable for demanding machining jobs.
A sharp diamond edge produces a surface that reflects light like a mirror. This finish is achieved directly during the milling phase, without relying on secondary grinding and polishing machines. It saves time and cost while keeping the part accurate.
Diamond milling allows engineers to cut plastics and tough materials to optical-grade quality. This transparency level can not be obtained through conventional tools.
Diamond Milling Process Steps For Cutting Profiles
The diamond milling follows a sequential process to cut the workpiece to the desired specifications. Here are the common steps involved.
- First of all, the jobpiece is secured firmly. Also, machinists remove any vibration sources.
- Next, a diamond-tipped cutter is installed. Here, the tool’s geometry is adjusted to mill the intended material.
- Then, the CNC machine is calibrated with sub-micron precision. Usually, a machinist uses high spindle speeds and low feed rates.
- After that, cutting starts in careful passes. Continuous lubrication is also introduced to avoid excessive heat generation.
- One-way tool paths keep cutting forces consistent and avoid surface errors.
- Finally, the last pass produces a surface roughness below 10 nm. This results in an optical-grade finish without the need for polishing.
Which Materials Are Suitable for Diamond Milling Cutters?

Diamond tools are used to cut a wide range of materials. It can mill brittle ceramics to soft polymers. The primary materials include:
- Ceramics
- Silicon
- Polycarbonate
- PMMA (Plexiglass)
- Aluminium
- Copper
- Bronze
- Glass
- ABS
- Polyethylene
Benefits of CNC Diamond Milling for Custom Machining
CNC diamond milling has obvious benefits over old cutting tools. Such advantages are increased precision, extended tool life, and performance in various challenging uses.
Aluminium Milling with Diamond Tools
Diamond tools can withstand high cutting speeds and heat without getting dull. This renders them very effective in mass-scale aluminum milling projects. A single diamond insert has a much longer life than carbide. This reduces tool changes and increases efficiency.
Milling Hard Alloys and Ceramics
A diamond tool is the hardest among other materials. This allows it to precisely machine ceramics, carbides, and other hard alloys. Conventional equipment cannot cope in such circumstances, but diamond bits provide precise and consistent results.
Milling Crystalline Materials
Diamond tools cut glass, PMMA, and polycarbonate to optical-grade finishes with ultra-fine cutting edges. Diamond milling eliminates polishing and saves time and money.
Stability in Milling Processes
Diamond milling tool lasts 30 to 50 times longer than carbide tools. This can increase consistency in production and reduce total tool costs.
Surface Finish in Diamond Milling
Diamond milling makes mirror-like surfaces more precise than can be achieved with other means. The process results are exact, and the finish is typically so clean that it may not require any further work.
Diamond Milling Techniques In Precision Machining
Most machining methods that use diamonds are linked to grinding and polishing. Diamond milling, however, is closer to cutting. Here are the standard diamond machining techniques.
Single Point Diamond Milling
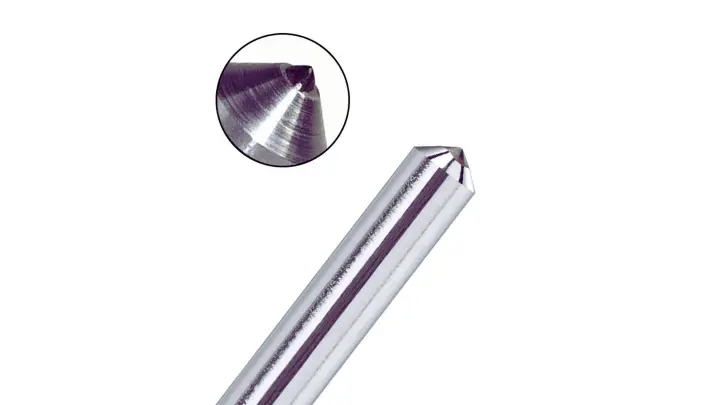

Single-point milling of diamonds employs a cutter with a single-crystal tip of diamond. It is machined on a fixed 5-axis machining centre. Therefore, it follows freeform paths with sub-micron accuracy. This technique works particularly well in machining glass, PMMA, and polycarbonate. Surface roughness to 10 nm Sa is achieved under optimised conditions, which is required in optical components and high-grade transparent parts.
Multi-Axis Diamond Milling
Freeform and curved surfaces with sub-micron accuracy are machined with a diamond tool on 5-axis ultra-precision machining centres. It is operated at spindle speeds exceeding 50,000 rpm and exceptionally low feed rates to maintain constant cutting forces. Under this arrangement, surface roughness values of less than 10 nm are regularly attained. Multi-axis diamond milling is used in optical and auto manufacturing parts like headlight lenses, light guides, and mirrors.
One-Way Milling Strategy
In diamond milling, it is essential to control vibration. Even the slightest vibration could ruin the quality of the surface and render a part useless. One-way milling is usually applied to overcome this. The cutter acts upon the workpiece in one direction, then withdraws and passes over, repeating the action. This maintains consistent cutting forces and reduces the tool deflection, achieving high-quality accuracy and surface finish.
Where Diamond Milling Delivers the Best Results
Diamond milling is highly adaptive when machining automotive lamp lenses, where size and complicated geometry render grinding infeasible. These parts can be machined to a mirror finish in one operation, with diamond tools on a 5-axis CNC setup.
It is also commonly used in light guides and other transparent optical devices. The thinness of the diamond cutter guarantees even surfaces and maintains highly accurate geometry.
Diamond Milling Tools For Cutting Complex Profiles
Diamond machining is based on specialised cutting inserts made of diamond. Tungsten carbide is typically used as the base, and a thin diamond coating is at the tip, giving it extreme hardness and long life. This equipment provides crisp and stable cuts and gives mirror finishes. Standard diamond milling tools include:
- One Point Diamond Cutters
- Diamond End Mills
- Diamond Fly Cutters
- Diamond Face Mills
- Diamond Coated Drills
When Diamond Milling Cannot Be Used?
Steel and iron alloys cannot be machined using diamond tools. These materials are rich in carbon, and this reacts adversely when cutting. The carbon atoms in the steel interlock with the diamond tip at high temperatures during machining. This results in bonding and sintering, sticking the tool to the workpiece and ruining the insert and the part.
Conclusion
Diamond Milling allows precise and high-quality machining of metals, plastics, and glass. It produces mirror-like surfaces and reduces the need for extra polishing. While it cannot be used on steel or iron, it excels with materials like aluminium, copper, titanium, PMMA, and polycarbonate. The process delivers accuracy, durability, and consistent results, making it a valuable solution for applications such as optical components and automotive parts.
How Diamond Milling Simplifies Cutting Hard Metals?