The reciprocating engine is a key component of a vehicle, and it consists of several critical parts, including the crankshaft. The crankshaft plays a vital role in converting the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which allows the engine to deliver power to the drivetrain. Without the crankshaft, the engine would not be able to function effectively.
So, if you are wondering what the crankshaft exactly is? How does it work? What are the types and components of crankshaft, and what does it cost? Just hold on, you are going to find the answer to each of these queries in detail.
Let’s get started.
What is Crankshaft?
A crankshaft is a rotating shaft that is driven by a crank mechanism. It converts the reciprocating motion of pistons into rotational motion. It is placed and operated in the engine block. Pistons are connected to the crankshaft with the help of connecting rods.
When pistons move up and down, the crankshaft changes the linear motion into rotational motion. This makes the flywheel move, which in turn transfers the power to the wheels of the vehicle.
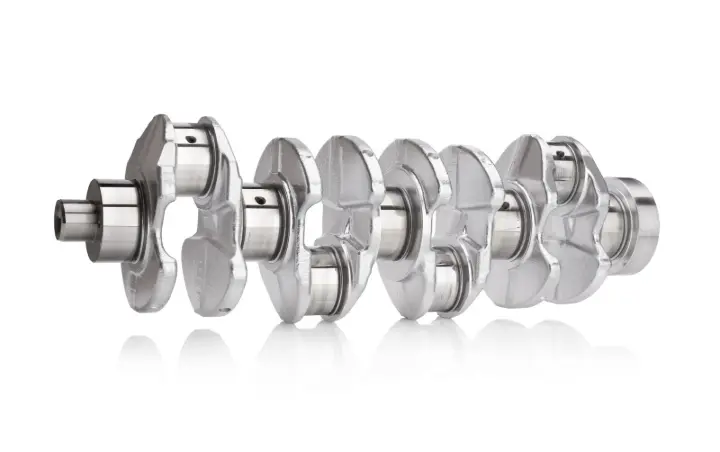

How Does Crankshaft Work?
The crankshaft works in a cycle along with the pistons. The pistons are pushed down after combustion in the four-stroke engine. As the pistons are connected with crankshafts with the help of rods, the connecting rod transfers this force to the crankshaft. It rotates and stores this energy in the flywheel.
As the crankshaft continues rotating, it also drives the pistons upward, helping to compress the fuel-air mixture for the next cycle. The process repeats and results in producing a smooth rotation that powers the car. Without the crankshaft, the up-and-down motion of pistons would be of no use.
What are the Types of Crankshafts
Crankshafts come in different types that depend on design and their uses. Here are some widely used crankshafts:
Cast Crankshaft
A cast crankshaft is one of the most common types used in engines. It is made by pouring molten metal into a mold. This type is cheaper and used in small and medium engines. It offers good strength for normal performance.
Forged Crankshaft
Forged crankshaft is another important type, which is well known for its strength. Manufacturers press solid steel into the desired shape using high pressure. They work well in heavy-duty engines and racing cars. This is because forged crankshafts can handle the stress easily.
Billet Crankshaft
There are also billet crankshafts, made from a single piece of steel using CNC machines. They are highly precise and durable, but cost more. These are often custom-made for special engines.
Flat-Plane Crankshaft
Flat-plane crankshafts are lighter ones. They allow faster engine speed. Sports cars often use them because they give quick acceleration. However, they create more vibration compared to other types.
Cross-plane Crankshaft
Another design is the cross-plane crankshaft. It is heavier but runs smoothly. This type is common in large engines and provides better balance.
Components of a Crankshaft

A crankshaft is not a single piece of metal; instead, it is made up of different parts. They work together to convert piston motion into rotation. Each part has its own role in keeping the engine smooth and powerful.
1. Main Journals
The main journals support the crankshaft inside the engine block. They allow the shaft to rotate freely with the help of bearings.
2. Crankpins (Rod Journals)
These are the parts where the connecting rods attach. They convert the up-and-down piston motion into a rotating motion.
3. Crank Webs
Crank webs connect the crankpins and main journals. They provide strength and stability to the crankshaft.
4. Counterweights
Counterweights help balance the vibrations that are produced by the engine. They reduce stress on the crankshaft and bearings.
5. Oil Passages
There are some small holes inside the crankshafts. They serve as oil passages. They allow engine oil to flow and keep all moving parts lubricated.
6. Flange
The flange is the part that connects the crankshaft to the flywheel. This link is important for transferring rotation to the transmission.
7. Nose (Snout)
The crankshaft nose extends from the front. It holds the timing gears.
Crankshaft Layouts
Engines use different crankshaft layouts. Inline engines use straight crankshafts. V6 engines use a special V-shaped design for balance. V8 and boxer engines use layouts made for high performance and smooth running. Each layout suits a different type of vehicle.
Crankshaft Lubrication
Lubrication is important for crankshaft life. Engine oil flows through small drilled holes inside the crankshaft. This oil reduces friction, prevents wear and tear, and keeps the shaft cool while moving. The crankshaft would not be able to move smoothly due to heat and friction without lubrication.
Materials Used in Crankshaft Manufacturing
Manufacturers use different strong metals for crankshafts. Normally, cast steel, forged cast steel, and forged alloy steels are used to manufacture crankshafts.
- Forged cast steel crankshafts are stronger and common in modern engines.
- Forged alloy steels are used for heavy-duty engines.
How Crankshafts are Made
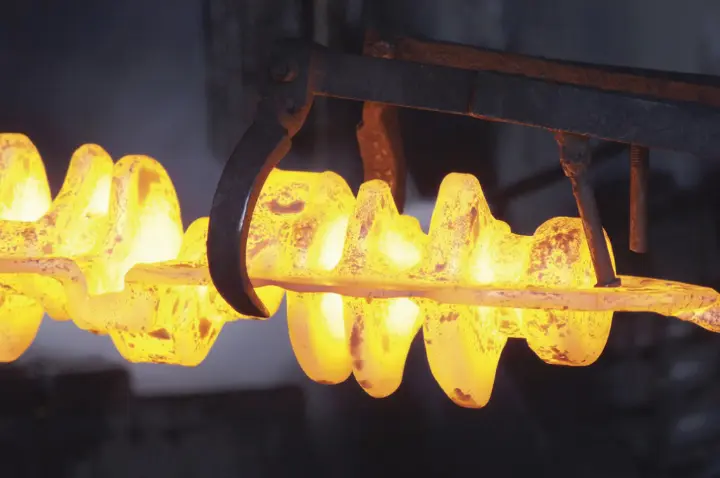

Crankshafts are made with two main methods: casting and forging.
- In casting, molten iron is poured into a mold to form the crankshaft.
- In forging, a block of steel is heated and shaped under high pressure.
After shaping, the crankshaft goes through machining, grinding, and heat treatment. Modern CNC machines provide the precision needed for smooth operation.
Faults and Failures in Crankshafts
Crankshafts can develop problems over time. Poor lubrication causes wear and tear in journals. Fatigue cracks are also common.
They can happen due to stress and repeated use. Oil seals may fail, resulting in leakage problems. Regular oil changes and proper maintenance prevent most of these issues.
Crankshaft Cost
The crankshaft cost depends on the type, size, and material used. When buying the new ones, cast crankshafts are cheaper, while forged and billet ones cost more. If we talk about the cost of replacement, then Labor also affects the total price because mechanics must remove and reinstall the engine.
Another important factor in costing is the engine’s condition. Sometimes bearings, seals, or rods also need replacement. In such cases, the overall cost increases.
Why CNC Turning Matters in Crankshaft Manufacturing
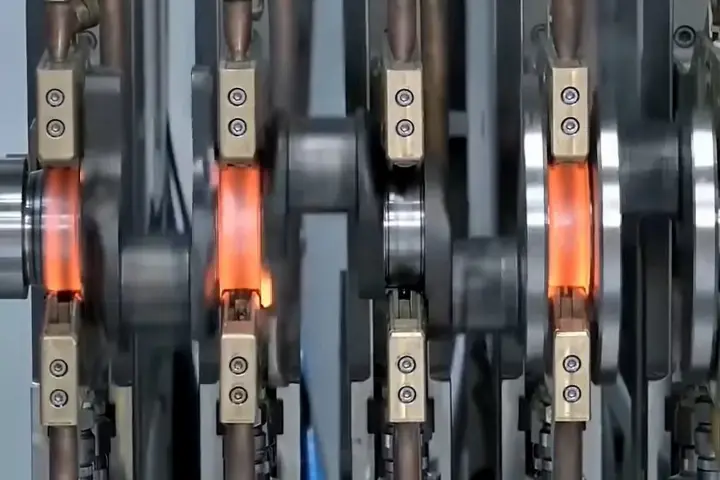
Modern crankshaft production uses CNC turning service instead of traditional methods. This is due to the number of advantages that come with it. CNC machines play a vital role in cutting crankshafts with high accuracy. This makes sure the overall shape is perfect, including every journal, pin, and flange, which fits perfectly.
It also reduces machining time and improves durability. That is why industries prefer CNC machining for custom crankshafts and high-performance parts.
Conclusion
The crankshaft is the heart of the engine, responsible for converting piston movement into power. We explored what is crankshaft, how it works, its types, components, and cost factors. We also saw how modern CNC turning service improves quality and accuracy.
A well-made crankshaft ensures smooth power and long engine life. With proper care, it will keep your vehicle running for years.
What is Crankshaft: Parts, Types & Cost Explained